Migration from MariaDB to MySQL
MySQL is the world’s most popular open source database. Migrating from MariaDB to MySQL provides the following benefits:
Business benefits:
- Eliminate vendor risk: MariaDB Corporation had a failed SPAC IPO, major restructuring, layoffs, and jettisoned key products. With MySQL, you have the proven financial stability of Oracle.
- Eliminate 3rd party risk: MariaDB relies of various 3rd parties for core technology. What happens when those 3rd parties are acquired or change directions? With MySQL, 100% of the product is developed by the MySQL Engineering Team at Oracle.
- Leverage GenAI and ML applications: After their recent restructuring and layoffs, MariaDB has limited resources to deliver on key new database capabilities. With MySQL, the MySQL HeatWave service provides the best of Analytics, Machine Learning, and GenAI in one database to power your next-gen applications.
Technical benefits:
- Drive the MySQL Roadmap: With the restructuring and layoffs at MariaDB Corporation, they have limited resources to drive their roadmap. The MySQL Roadmap is aggressively delivering new capabilities for our customers.
- 100% Developed by MySQL: MariaDB relies on various 3rd parties for core technology. MySQL is 100% developed by the MySQL Engineering Team at Oracle.
- Build GenAI and ML applications: When you want to build Analytics, Machine Learning, and GenAI applications, MariaDB does not have the resources to keep up with the rapid pace of innovation. MySQL and MySQL HeatWave provide a complete solution in a single database.
MySQL: The World's Most Popular Open Source Database
MySQL is the world's most popular open source database because of its reliability, high-performance, and ease of use. MySQL combines the benefits of a widely adopted open source database with high quality, 24x7 support, training and consulting services delivered by Oracle, the world's leader in database technology. As a result, MySQL users benefit from both a strong ecosystem, with millions of users, as well as the backing of the world's leading database company that has the proven ability to support its customers' mission critical database applications worldwide.
MariaDB is NOT MySQL! MariaDB is a fork of MySQL and is not compatible with MySQL. Since MariaDB 10.0, MariaDB has diverged significantly and none of the modern innovations in MySQL, such as the Transactional Data Dictionary, Group Replication, InnoDB Cluster, Shell, DocStore, or XProtocol are available in any version of MariaDB. By choosing MariaDB, customers risk being locked into a downstream fork of MySQL, whose future is at risk.
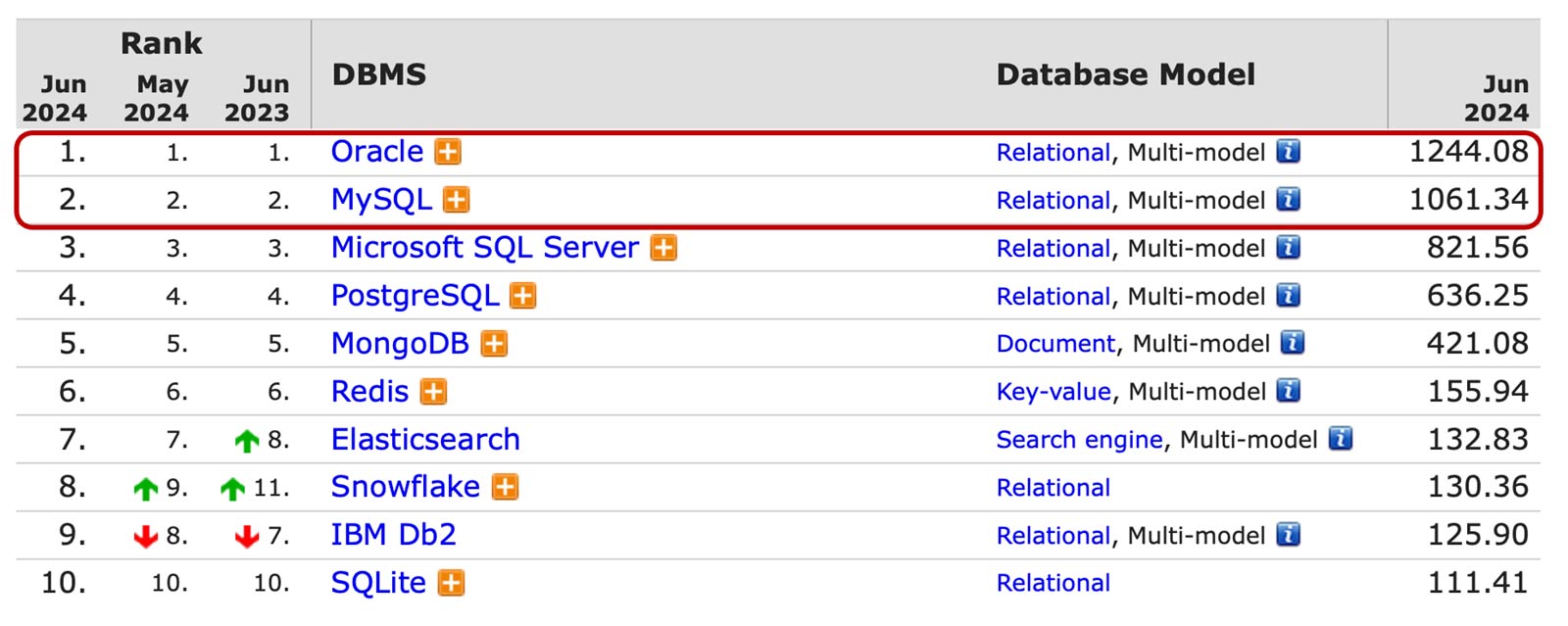
According to DB-Engines, MySQL is the world's most popular open source database. In fact, the world's #1 and #2 most popular databases are developed at Oracle. On the other hand, MariaDB is not in the Top 10 most popular databases.
MySQL is Financially Secure
MySQL is part of Oracle, a publicly traded company with stable revenue and recognized for delivering decades of database innovations. Oracle continues to make major investments in MySQL Engineering Development and Support.
MariaDB Corporation is experiencing major financial difficulties. Their IPO was a SPACtacular failure. In 2023, MariaDB went IPO via a SPAC acquisition while losing millions of dollars a year:
- MariaDB's SPAC was a disaster
- MariaDB stock fell 60% in just over a day of trading
- MariaDB is ditching strategic products and cutting 28 percent of the workforce
- MariaDB cuts jobs, repeats 'going concern' warning to stock market
- JPM, Goldman Cut Ties With Angel Pond-MariaDB Deal
MySQL is Upstream and Drives the MySQL Product Roadmap
MySQL develops and maintains its own database technology. The upstream MySQL Product Roadmap is controlled and defined by MySQL Engineering & Product Management, in concert with MySQL Support, MySQL Customers, and users.
MariaDB chose to diverge from MySQL and can no longer deliver drop-in compatibility. None of the modern advances in MySQL are available in any version of MariaDB. Due to their choice to diverge from upstream MySQL and its lack of engineering resources, MariaDB must rely on small 3rd party technology provides for its core database technology. For example, MySQL provides InnoDB Cluster and InnoDB ClusterSet based on Group Replication, built natively into the MySQL Server. MariaDB does not provide its own native HA database technology but instead relies on a 3rd party. That means that MariaDB is not in control of its high availability roadmap, bug fixes, or version compatibility.
MySQL Core Technology is 100% developed by MySQL
MySQL core technology, such as InnoDB, the core transactional database engine, is developed by the MySQL team. MySQL delivers enhancements, bug fixes, and ensures compatibility between versions.
MariaDB relies on the goodwill of third parties for its core technology, including from companies it competes with, e.g., Percona (XtraBackup), Codership (Galera), Spider Engine, etc. What will happen when some of these third parties are acquired or change priorities?
Backed by the MySQL Engineering Team
Oracle has made significant investments in MySQL Engineering and Support. MySQL has more engineers for R&D and more Support Engineers to help customers.
The size of MariaDB's engineering team is much smaller and shrinking. After its failed IPO, MariaDB was forced to cut its workforce by 28% and stop selling strategic products including the SkySQL database service. What will MariaDB cut next?
MySQL is “NoSQL + SQL”
With MySQL, developers can use a single database for SQL and NoSQL database applications. Rather than rely on separate databases for SQL relational and schema-less JSON documents, MySQL Document Store enables organizations to use MySQL to consolidate their relational and document database workloads.
While MariaDB has support for the JSON document type, it does not have Document Store or XProtocol capabilities, forcing customer look elsewhere for their NoSQL document database applications.
MySQL HeatWave Database Service: OLTP, OLAP, Machine Learning, GenAI
MySQL HeatWave is a fully managed database service from the MySQL Team, that includes:
- MySQL HeatWave GenAI for integrated and automated generative AI
- MySQL HeatWave AutoML to automate the machine learning pipeline
- MySQL HeatWave Lakehouse to query data in object storage and MySQL
- MySQL HeatWave to accelerate query performance
MariaDB SkySQL was a strategic database cloud service released in 2020. After its failed IPO, MariaDB was forced to cut its workforce by 28%, stop selling the SkySQL database service, and issue a "going concern" warning over its financial viability.
- MariaDB cuts jobs, repeats 'going concern' warning to stock market
- Analysts scratch heads over MariaDB's decision to ditch DBaaS crown jewels
- MariaDB’s Bad Week: Layoffs and an End to Azure Support
- Azure dropping database support for MariaDB. Users advised to migrate to MySQL
How can organizations trust MariaDB Corporation given their ongoing financial instability and uncertainty?
Additional Resources
- Customer Success: Great Healthworks Improves Reliability by Migrating from MariaDB
- On Demand Webinar: Migration from MariaDB to MySQL
- White Paper: Migrate from MariaDB to MySQL
- On Demand Webinar: Migrate from MariaDB to MySQL HeatWave
- White Paper: Migrate from MariaDB to MySQL HeatWave on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
- Blog: Migrate from MariaDB to MySQL HeatWave: easier with MySQL Shell